- Author Maria Gibbs gibbs@autolifeadvice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 03:05.
- Last modified 2025-01-22 17:48.
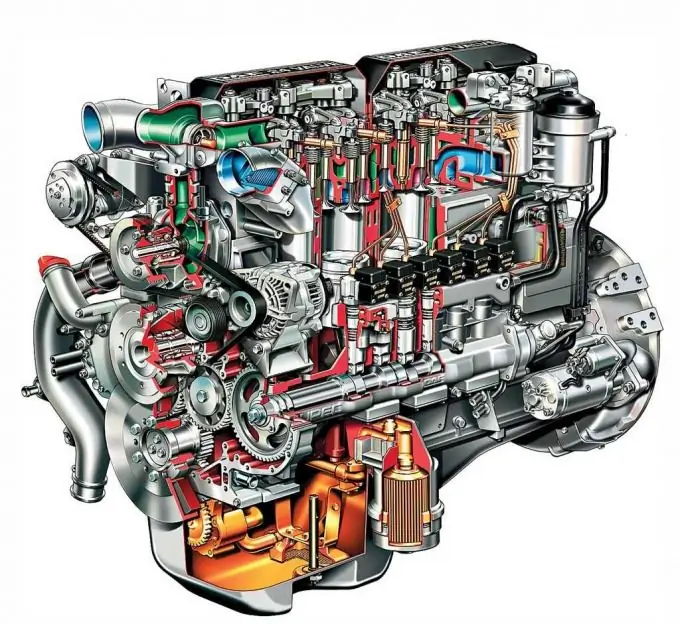
The undoubted advantages of diesel engines: high torque and efficiency. Cons: low power and resource. Therefore, engineers are striving to increase the power of diesel engines …
Instructions
Step 1
Increasing the compression ratio The compression ratio directly affects the combustion efficiency. The higher the compression ratio, the less fuel the same power will be achieved. Diesel engines typically use compression ratios between 18: 1 and 22: 1, which explains their superior performance over gasoline engines. The full realization of these advantages is facilitated by the absence of a throttle valve on diesel engines. For example, increasing the compression ratio by only one gives an increase in power of 2%.
However, increasing the compression ratio does not always lead to an increase in power. If the compression ratio is near the knock limit for a given fuel type, then a further increase in the compression ratio will degrade the power and reliability of the engine.
Step 2
Common Rail System This system has been used in diesel power systems since 1997. Common Rail is a method of injecting a fuel mixture into the combustion chamber at high pressure, regardless of load or engine speed. It differs from the previously used injection pump system in that it creates pressure exactly at the moment of fuel injection into the combustion chamber, and not inside the intake manifold. This allows the fuel mixture and combustion parameters to be optimized separately for each cylinder. The system gives an increase in power up to 30%. The specific rate of power increase for each diesel engine with common rail depends largely on the injection pressure. In third-generation Common Rail systems, the injection pressure is around 2000 bar. The fourth generation of Common Rail systems with an injection pressure of around 2,500 bar will be launched shortly.
Step 3
Turbocharging is an effective and common means of increasing the power of both diesel and gasoline engines. The turbine supplies additional air to the cylinders, which allows for increased fuel delivery and, therefore, increased power. Taking into account that the exhaust gas pressure of a diesel engine is 1.5-2 times higher than that of a gasoline engine, the turbocharger works more efficiently on diesel engines: it provides boost from the lowest rpm and does not have a characteristic failure after a sharp depression of the accelerator pedal - turbo lags. The lack of a throttle valve in a diesel engine eliminates the need for a complex turbine control circuit. A charge air intercooler (intercooler) installed in tandem with a turbocharger makes it possible to further improve the filling of the cylinders and obtain a power increase of 15-20%. Another advantage of turbocharging on a diesel engine: it does not lose power when operating in high mountain areas.
Step 4
Chip tuning In this case, the power of the diesel engine is increased by installing an electronic corrector for the parameters of the injection timing, injection duration (fuel mixture composition) and an increase in boost pressure. Modern chip kits made using advanced technologies allow increasing the power of the turbodiesel engine by 25-35% and reducing fuel consumption by 10%.
The installation of such kits does not require special skills, any additional refinement, are equipped with detailed installation instructions and are intended for self-installation by the owner of the car, even if he does not have detailed knowledge of the device.






